Data Archiving Overview¶
With EnOS Data Archiving Service, users can configure scheduled data archiving tasks to archive data from real-time message channels, offline message channels, or alarm databases to more cost-effective storage solutions, achieving data backup purposes.
The major components and architecture of the Data Archiving service is shown in the figure below.
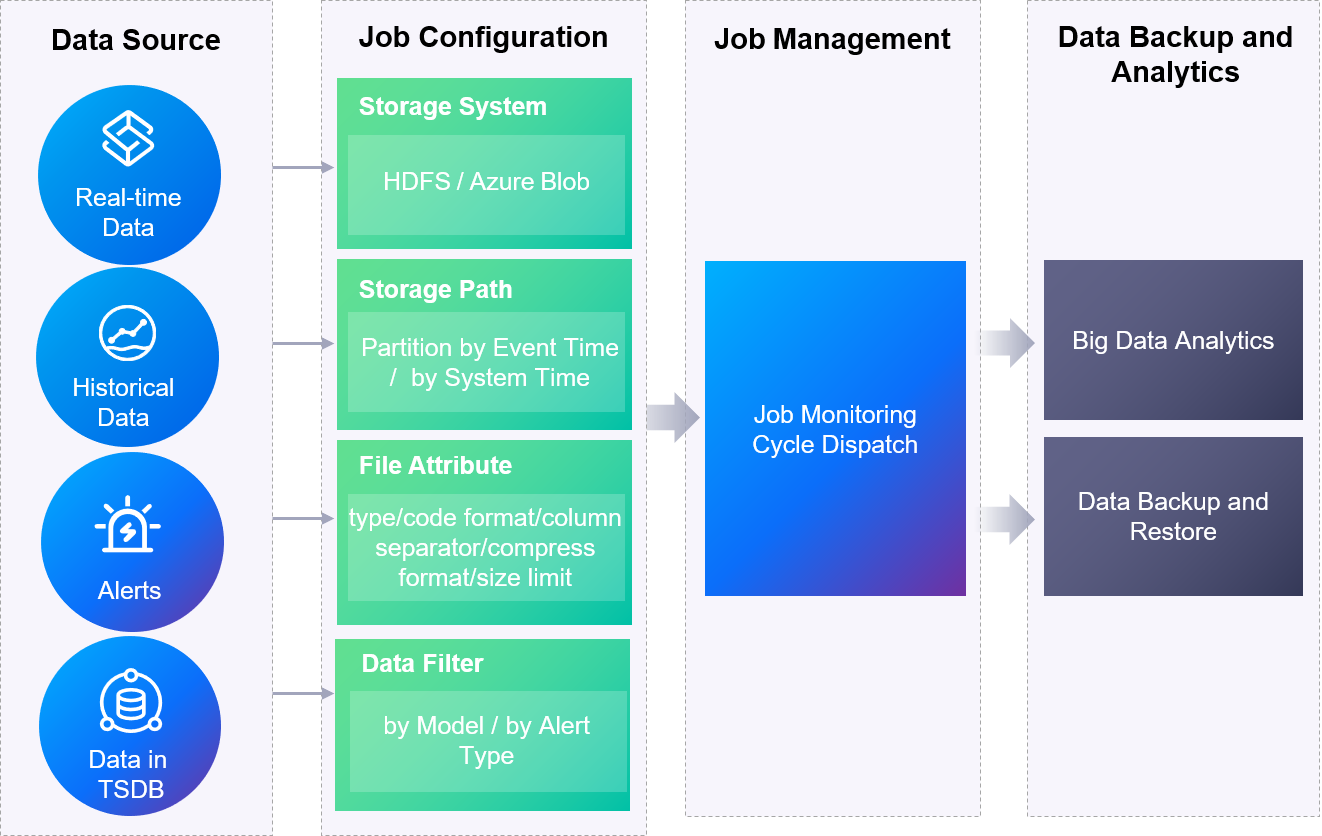
Description to the architecture components
Data Source: Support archiving real-time device data, historical data integrated from stream data processing and offline channel, alarm data.
Job Configuration: Support configuration of the storage system, storage path, and file attributes, as well as filtering data to be archived by device models and alert types. For more information, see Data Archiving Reference.
Job Management: Support data archiving job monitoring and scheduling.
Data Archiving Storage: Support archiving data to more cost-efficient storage solutions.
Product Advantages¶
Provide an economical and reliable solution formassive cold data storage, preparing for future data mining
Support multiple data sources
Support multiple data filtering rules
Support selecting suitable storage media on demand
Usage scenarios¶
Enterprises, as data owners, can archive business data (cold data) that is infrequently accessed but occupies significant storage space to reduce storage costs, while retaining it for potential future use by data consumers.
Main Functions¶
Archiving Real-time Data and Offline Data: The Data Archiving Service supports the archiving of both real-time data ingested from devices or generated by stream processing jobs of specified models and data integrated from the offline message channel.
Archiving Real-time Alert Records: The Data Archiving Service supports the archiving of specified fields of real-time alert records (both history and active alert records) of specified models.
Setting the Properties of Archived Files: Properties of archived files, including file type, encoding, column delimiter, compression, and size limit, can be set based on your data usage scenarios. In this way, the archived files will be ready for future development and analysis.
Customized Archiving Cycles: You can set customized data archiving cycles (1 hour, 12 hours, or 24 hours) based on the data amount and business requirements on data archiving efficiency. The longer the archiving cycle is, the more data can be processed in the cycle, and the number of small files caused by data latency can be significantly reduced.
Setting the Storage System and Path: The archived files will be synchronized to the specified storage system and stored in the configured path, thus achieving data backup.